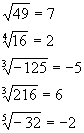Nth Roots of a Real Number and Radicals

We say b is an nth root of a number a if and only if
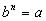
| Number |
Square Root |
| 36 |
6 or -6 |
| 100 |
10 or -10 |
| 0 |
0 |
| -4 |
No real square
root |
| Number |
Cube Root |
| 27 |
3 |
| 125 |
5 |
| -8 |
-2 |
| -64 |
-4 |
| Number |
Fourth Root |
| 81 |
3 or -3 |
Note: Some numbers have two real nth roots while some have
only one real nth root. The principal nth root of a is defined to
be the positive nth root if two real nth roots exist, the real
nth root if only one exists.
We denote the principal
nth root of a by
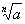
N is called the index or order
of the radical, a is the radicand, and the symbol given
below is a radical symbol.
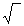
Remark: If no indes is written,
the index is assumed to be two.
Examples:
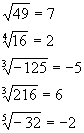
Properties of Radicals
In what follows each radical represents a real number.
I. If n is even
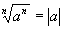
if n is odd
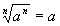
II. Product Property
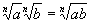
III. Quotient Property
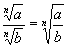
IV. Root Property
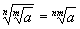
Copyright © 1995 - Present. SSmyrl
|